inajmi
Member
- Downloaded
- 21.6 GB
- Uploaded
- 71.2 GB
- Ratio
- 3.29
- Seedbonus
- 5,495
- Upload Count
- 0 (0)
Member for 9 years
Network Virtualization with Hyper-V
With the power of network virtualization you can create multi-tenant environment and assign virtual machines or group of virtual machines to different organizations or different departments. In a traditional network, you would simply create different VLANs on physical switches to isolate them from the rest of the network(s). Likewise, in Hyper-V, you can also create VLANs and virtual switches to isolate them from the network in the same way.
Readers can also refer to our
For example, you can configure a group of virtual machines on the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet and other group of virtual machines on 192.168.2.0/24 subnet.
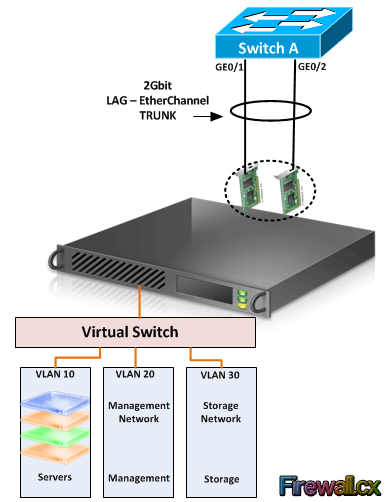
Each virtual machine can have more than one virtual network adapter assigned to it. Like regular physical network adapters, the virtual network adapters can be configured with IP addresses, MAC addresses, NIC teaming and so on. These virtual network adapters are connected to a virtual switch. A Virtual switch is a software version of physical switch that is capable of forwarding traffic, VLAN traffic, and so on. The virtual switch is created from within the Hyper-V Manager and is then connected to one or more available physical network adapters of the host machine. The physical network adapters on the host machine are then connected to physical switch on the network.
As shown in figure 1.3, three VLANs are created under same virtual switch. The host is then connected to the physical switch by usually combining the multiple physical network cards into one also called LAG (Link Aggregation Group) or EtherChannel (Cisco’s implementation of LAG) interface. LAG or EtherChannel combines the speed of both physical network adapters. If for example we have two 1Gbps physical network cards, with the use of LAG or EtherChannel, these are combine into a single 2Gbps network card.
Microsoft’s Hyper-V supports the creation of three different types of virtual switches:
VDI is a new way of delivering desktops to end users. In VDI, virtual desktops are hosted centrally as virtual machines and are provided or streamed to users via the network or Internet using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) service. These virtual desktops can be used or accessed by users with different types of devices like, PCs, laptops, tablets, smart phones, thin clients, and so on. VDI have created a new hype of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) concept. With BYOD policy implemented in the organization, users can bring their own devices like laptops, tablets, etc. and the company delivers the required virtual desktop via the network infrastructure.
VDI is an upcoming trend that offers many advantages such as:
VDI is fully supported and can be implemented in Windows Server 2012 by installing Remote Desktop Services server role and configuring the virtualization host. You can create virtual machines running Windows XP/7/8 and easily assign the virtual machines to users.
We’ve covered a few of the important virtualization features deployable with Windows Server 2012 and
With the power of network virtualization you can create multi-tenant environment and assign virtual machines or group of virtual machines to different organizations or different departments. In a traditional network, you would simply create different VLANs on physical switches to isolate them from the rest of the network(s). Likewise, in Hyper-V, you can also create VLANs and virtual switches to isolate them from the network in the same way.
Readers can also refer to our
You must be registered for see links
that analyses the concept of
You must be registered for see links
.For example, you can configure a group of virtual machines on the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet and other group of virtual machines on 192.168.2.0/24 subnet.

Each virtual machine can have more than one virtual network adapter assigned to it. Like regular physical network adapters, the virtual network adapters can be configured with IP addresses, MAC addresses, NIC teaming and so on. These virtual network adapters are connected to a virtual switch. A Virtual switch is a software version of physical switch that is capable of forwarding traffic, VLAN traffic, and so on. The virtual switch is created from within the Hyper-V Manager and is then connected to one or more available physical network adapters of the host machine. The physical network adapters on the host machine are then connected to physical switch on the network.
As shown in figure 1.3, three VLANs are created under same virtual switch. The host is then connected to the physical switch by usually combining the multiple physical network cards into one also called LAG (Link Aggregation Group) or EtherChannel (Cisco’s implementation of LAG) interface. LAG or EtherChannel combines the speed of both physical network adapters. If for example we have two 1Gbps physical network cards, with the use of LAG or EtherChannel, these are combine into a single 2Gbps network card.
Microsoft’s Hyper-V supports the creation of three different types of virtual switches:
- Internal: - The internal virtual switch can communicate only between virtual machines. A common example is a cluster based system where virtual servers connect with each other through a dedicated network connection. Internal virtual switches do not connect to the physical network infrastructure (e.g switches).
- External: - The external virtual switch can communicate directly with the physical network infrastructure. The virtual switch is used to for the seamless communication between the virtual machines and the physical network.
- Private: - The private virtual switch can communicate between virtual machines and the physical host only (physical hardware server).
VDI is a new way of delivering desktops to end users. In VDI, virtual desktops are hosted centrally as virtual machines and are provided or streamed to users via the network or Internet using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) service. These virtual desktops can be used or accessed by users with different types of devices like, PCs, laptops, tablets, smart phones, thin clients, and so on. VDI have created a new hype of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) concept. With BYOD policy implemented in the organization, users can bring their own devices like laptops, tablets, etc. and the company delivers the required virtual desktop via the network infrastructure.
VDI is an upcoming trend that offers many advantages such as:
- Central management and control
- Low cost since there is no need of desktop PCs. Alternate devices such as thin clients usually preferred
- Low power consumption. Tablets, thin clients, laptops require low power compared to traditional desktop or tower PCs
- Faster desktop deployments
- More efficient backup
VDI is fully supported and can be implemented in Windows Server 2012 by installing Remote Desktop Services server role and configuring the virtualization host. You can create virtual machines running Windows XP/7/8 and easily assign the virtual machines to users.
We’ve covered a few of the important virtualization features deployable with Windows Server 2012 and
You must be registered for see links
, that allow organizations to consolidate their server, network and desktop infrastructure, into a more efficient model.